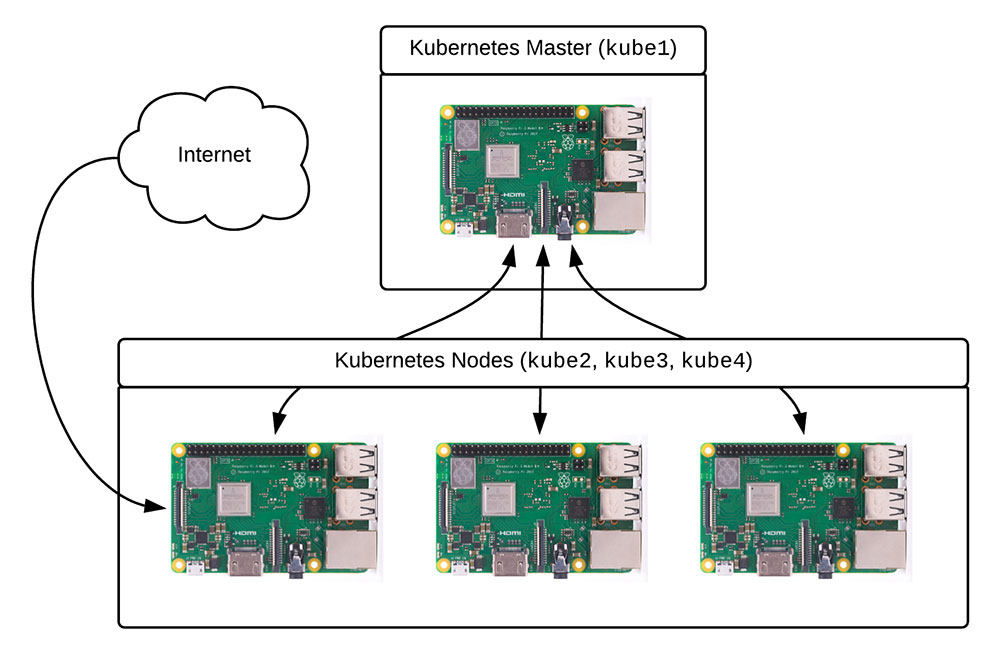
Here’s the overall cluster architecture we’re targeting:
Once all the Pis are online and operational, you need to copy the included example.config.yml file to config.yml and modify it to suit your needs (especially consider changing salt and password-related variables!).
Next, run ansible-galaxy install -r requirements.yml --force to install Ansible role dependencies.
Then, run pip install openshift to make sure the appropriate Kubernetes-controlling Python libraries are present.
Finally, run the Ansible playbook to provision the Raspberry Pis:
$ ansible-playbook -i inventory main.yml
After 10-20 minutes, you should see a summary of the completed tasks:
PLAY RECAP *******************************************************
kube1 : ok=118 changed=59 unreachable=0 failed=0
kube2 : ok=73 changed=41 unreachable=0 failed=0
kube3 : ok=73 changed=41 unreachable=0 failed=0
kube4 : ok=73 changed=41 unreachable=0 failed=0
At this point, Kubernetes, Drupal, MySQL, Traefik, and all the other supporting systems should be present. It can take a few minutes after these configurations are present before Drupal is able to be installed, because Kubernetes will now start the process of pulling all the relevant Docker images, starting all the right containers, and connecting everything together!
To re-provision a Pi (e.g. if you were messing with it and screwed up something on the image), you should reimage the microSD card with a fresh copy of Raspbian Lite, and reconfigure the Pi's networking, then run this main playbook again. Note that if you screw up the Kubernetes master (
kube1), it might be best to re-image the whole cluster :)
Managing the Kubernetes Cluster
You can SSH into the Kubernetes master (10.0.100.61 by default) and run kubectl by switching to the root user (sudo su). For example:
kubectl get nodes kubectl get pods
The Ansible playbook also copies the config file locally, so you can run kubectl locally if you have it installed. Just export the path to the file (e.g. export KUBECONFIG=~/.kube/config-dramble-pi), then you can run kubectl commands.
Accessing the Default Drupal site on the Cluster
Edit your /etc/hosts file and add the line:
10.0.100.62 cluster.pidramble.test
Now you can access the drupal Kubernetes service at the URL: http://cluster.pidramble.test/. To install Drupal, follow the steps in Drupal's installation wizard.
Note that for the hosts file, you can point the domain at any of the non-master nodes (e.g.
10.0.100.62,10.0.100.63, etc.); they are all running the Traefik ingress controller as a Kubernetes DaemonSet, meaning any single host can direct traffic on port 80 to thedrupalservice. Technically, you could use DNS round robin to point one domain at all the Pis, but the best solution is to have another load balancer in front of all the Pis (as you can do if you have a Drupal Pi running separately), redirecting the traffic to them using a more intelligent load balancing and health monitoring solution.
Raspberry Pi image used in architecture diagram from Raspberry Pi Foundation website.